Bones of Upper Extremity
- The part of the body that includes the arm, wrist, and hand comprises of ” The Upper Extremity”.
- Each upper limb is made up of 32 bones.
- The pectoral girdle consists of 2 bones: the scapula, also called the shoulder blade, and the clavicle, also known as the collarbone. Then there’s the arm, which only has one humerus, one radius, one ulna and the bones of the wrist ( carpals , metacarpals and phalanges).
The Shoulder Joint Complex
The Shoulder Complex is a multi-joint structure that provides the link between the thoracic cage and the upper extremity.
The shoulder has a high degree of mobility but this region is very unstable. The bones of the shoulder region include the humerus, scapula and clavicle.
The shoulder region is a complex of four joints:-
- Glenohumeral Joint
- Acromio-Clavicular Joint
- Sterno-Clavicular Joint
- Scapulothoracic Joint
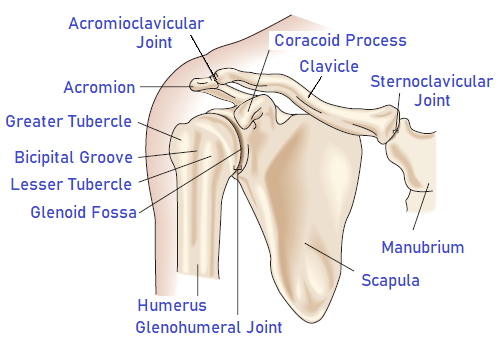
Scapula, Clavicle & the Shoulder Joints:-
- The Scapula: The Scapula is a large triangular bone that rests on the posterior thoracic cage between the second rib and the seventh rib in the normal position. The
glenoid fossa of the scapula faces anterolaterally. - The Clavicle: The clavicle runs obliquely at 60 to the scapula and provides the link between the upper extremity and the axial skeleton.the inner surfaces of the costal cartilages on the 6th rib. The acromion process is located at the superior aspect of the scapula and articulates with the clavicle.
- The Humerus:The humerus is a long bone and is the major bone of the arm. The humeral head is rounded and articulates with the glenoid fossa of the scapula.
- Glenohumeral Joint : The glenohumeral joint is a ball-and-socket joint and is a freely moveable joint in the body. It is formed by the articulation of the spherical head of the humerus with the pear-shaped glenoid fossa of the scapula. from superior anterior ribs.
- Acromio-Clavicular Joint: The acromioclavicular joint is a plane synovial joint formed of the articulation of the acromion and the distal end of the clavicle.
- Sterno-Clavicular Joint: The sternoclavicular joint, the articulation of the proximal clavicle with the sternum and cartilage of the first rib, is a saddle synovial joint. It provides the only bony connection between the humerus and the axial skeleton.
Functions of the Clavicle:-
- The clavicle provides protection for the neural bundle called the “brachial plexus,” the vascular system supporting the upper extremity; supports the weight of the humerus; and helps maintain the position of the scapula and the humerus.
The Scapulothoracic Joint:-
- The scapulothoracic joint is not a true joint, but a physiological (“functional”) joint. It is formed by the articulation of the scapula with the thoracic cage.
- Any movement of the scapulothoracic joint results in movement of the acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and glenohumeral joints. The scapulothoracic joint provides mobility and stability for the orientation of the glenoid fossa and the humeral head for arm movements in all planes.
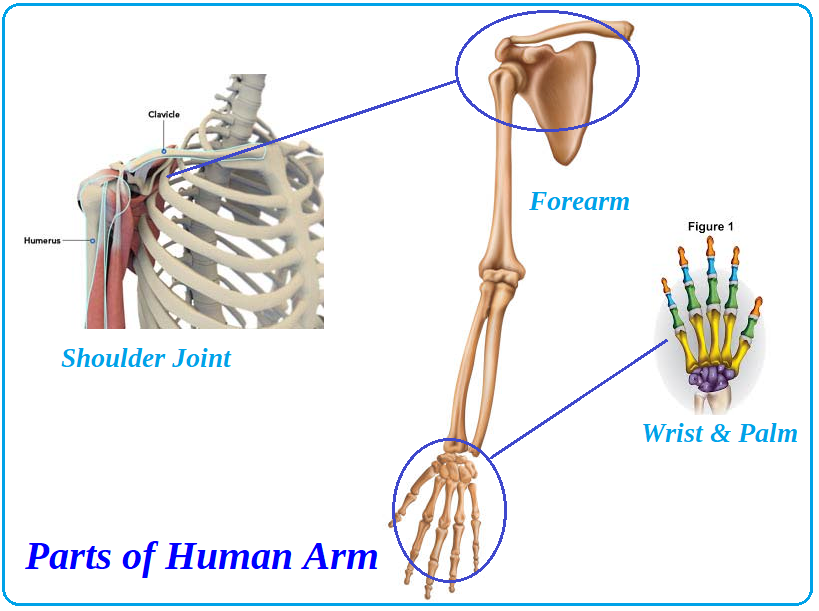
The Human Arm:-

Each arm has 8 carpal bones, 5 metacarpals and 14 phalanges
The human arm consists of the
- Humerus
- Radius
- Ulna
- Carpals
- Metacarpals
- Phalanges.
.
The Bones of the Human Arm:- Humerus
- The Humerus is the longest and largest bone of the upper limb.
- It consists of a proximal end, a shaft and a distal end.
- The humerus articulates with the glenoid fossa of the Scapula at the glenohumeral joint and so it helps in the movements of the shoulder.
- The humerus also articulates at the distal end with the radius and ulna at the elbow joint.
- The thick triangular deltoid muscle spanning over the clavicle, acromion and scapula inserts into the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus.
- The olecranon articulates with the Humerus via a deep triangular depression situated over the posterior surface of the humerus, known as the olecranon fossa .
- There is also a small depression at the anterior face of the humerus at its distal end called the coronoid fossa. It is the site where the coronoid process of the ulna rests at the time of flexing the forearm.
The Bones of the Human Arm:- Radius & Ulna
- The Radius and Ulna are long bones forming the forearm, that extend from the elbow to the wrist.
- The radius is shorter than the ulna . Its proximal end articulates with the humerus, and its broad distal end articulates with the carpal bones at the wrist.
- The ulna is the medial bone of the forearm and the longer of the two parallel forearm bones.
- Both the radius and ulna has three main parts: a proximal end ( upper extremity), shaft and a distal end ( lower extremity).
The Elbow Joint

- The elbow joint complex is a compound synovial joint that consists of two articulations: humeroulnar and the humeroradial.
- It helps in rotation during pronation and supination of the forearm.
- The distal humerus articulates with both the proximal ulna and proximal radius, and the two articulations are enclosed in a single synovial cavity.
- On the lateral side, the capitulum of the humerus articulates with the head of the radius to form the humeroradial joint; medially, the trochlea of the humerus articulates with the trochlear notch of the ulna to form the humeroulnar joint.
The Wrist & Palm
The wrist joint (radiocarpal joint) is a synovial joint is formed between the forearm and the hand.
The wrist is an ellipsoidal (condyloid) synovial joint, allowing for movement along two axes. This means that flexion, extension, adduction and abduction can occur at the wrist joint.
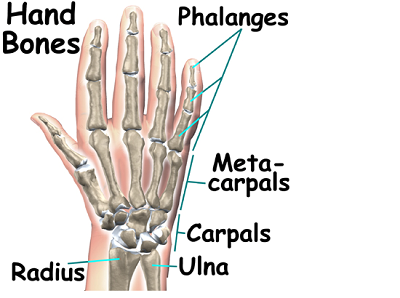
The 3 major types of bones in the hand are:
- Carpals- The 8 bones that make up the wrist.
- Metacarpals-. The 5 bones that compose the middle part of the hand.
- Phallanges- The 14 bones that are found in the fingers of each hand.