Basic Life Support For Children
(1 to Puberty)
- For children of all age groups, the compression to breaths ratio is 30:2 for one rescuer and 15:2 for 2 rescuers.
- For children, compress the chest at least one third (1/3) of the depth of the chest.This will be less than 2 inches for small children and approximately 2 inches for bigger children.
- If you find an unresponsive child, perform CPR for 2 minutes before you call EMS .
- Cardiac arrests are not common in children. They are mostly preceded by respiratory problems. Early intervention and prevention of respiratory issues improve the rate of survival.
Prevention is the first link in the Chain of Survival
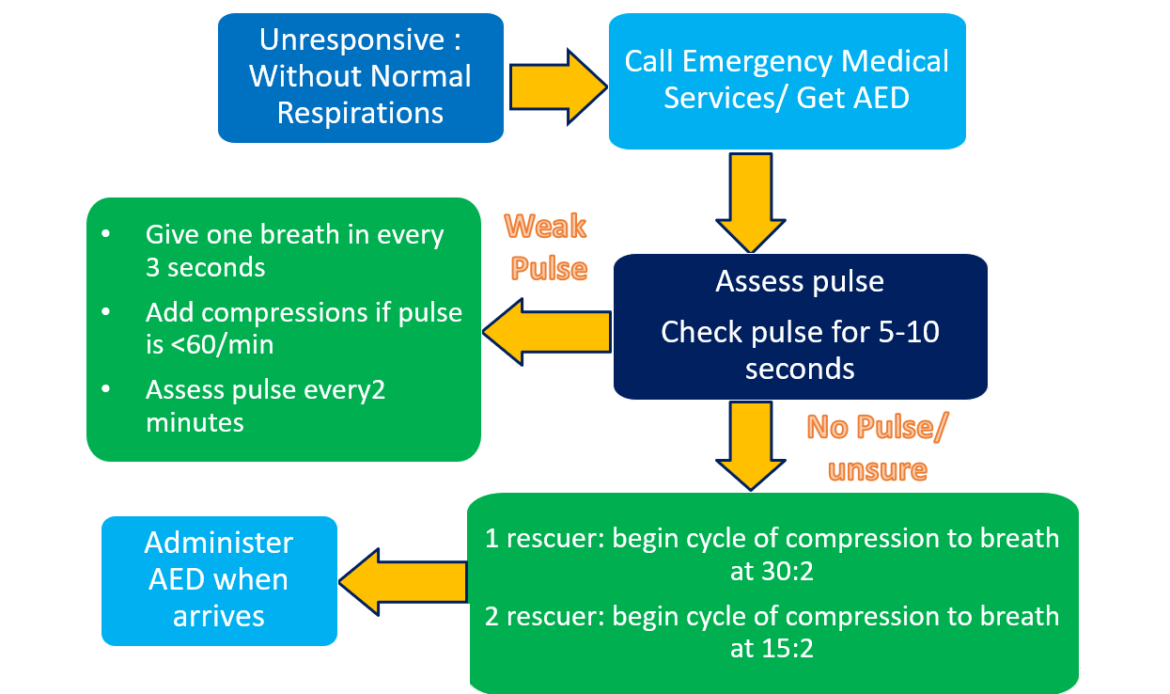
BLS Algorithm for Children
Criteria for High Quality CPR
- CPR rate is at least 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Compression depth is 1/3rd of the chest.
- Do not over-ventilate
- Minimum interruptions during chest compressions.
Steps of Basic Life Support for Children
- Talk loudly and tap the child to determine if they are responsive.
- If the child is non-responsive / not breathing or gasping, send someone to call EMS and to get an AED.
- Assess for breathing while checking for the child’s carotid pulse ( on the side of the neck) for 5 to 10 seconds, but not more than that.
- If you are unsure and are not getting the pulse, start CPR by doing 30 compressions followed by 2 breaths. For 2 rescuers, begin the CPR by doing 15 compression by one rescuer and 2 breaths by the second rescuer.
- After doing CPR for 2 minutes, and if other help has not arrived, call EMS while staying with the child. Get an AED if you know where one is.
- Use and follow AED prompts when available while continuing CPR until EMS arrives or the condition normalizes.
******* AED : Automated External Defibrillator
Steps of Basic Life Support for Infants
(0-12 months)
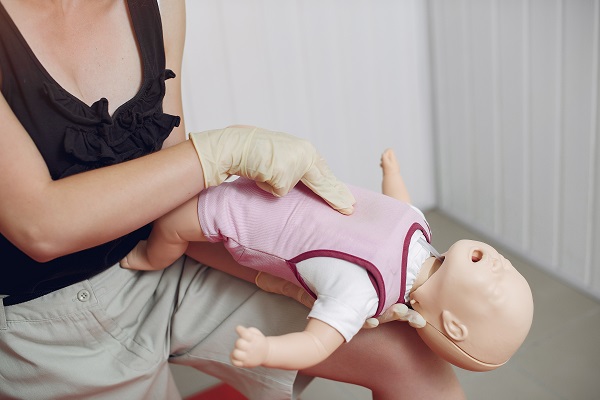
- To do CPR on infants, do the following:-
- Keep the infant face up on a hard surface.
- Using the fingers of your free hand provide chest compressions in the center of the chest.
- Do not press on the end of the sternum.
- Compression depth should be 1.5 inches and 100-120 compressions per minute.
-
- Tap the heel of their foot and talk loudly to determine if they are responsive.
- Assess if they are breathing while simultaneously checking for the infant’s brachial pulse for 5-10 seconds. If the child is non-responsive / not breathing or gasping, yell for help and send someone to call EMS and to get an AED.
- Assess for breathing while checking for the child’s carotid pulse ( on the side of the neck) for 5 to 10 seconds, but not more than that.
- If you are unsure and are not getting the pulse, start CPR by doing 30 compressions followed by 2 breaths. If you can feel a pulse but the rate is less than 60 beats per minute, begin CPR.
- After doing CPR for 2 minutes, and if other help has not arrived, call EMS while staying with the child. Get an AED if you know where one is.
- Use and follow AED prompts when available while continuing CPR until EMS arrives or the condition normalizes.
******* AED : Automated External Defibrillator


Comments (1)
temp email - April 4, 2025
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here The sketch is tasteful your authored subject matter stylish nonetheless you command get got an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this hike