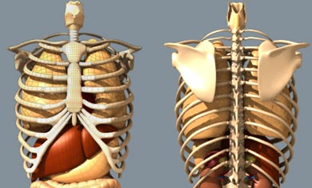
The Thoracic cage
- Thoracic Cage or Rib cage, in skeletal system is the bone structure that forms the chest, or thorax. It comprises of the ribs and their attachments to the sternum bone and vertebral column. The ribs along with their sternum connectivity forms a cage like enclosure which encases and protects some of the vital organs of the human body.
- The ribs are connected to the sternum with a flexible tissue called cartilage. The rib cage protects the organs in the chest, such as the heart and lungs.
The Ribs
- The ribs are a collection of 12 pairs of long, curved bones which are connected to the spinal vertebrae posteriorly and to the sternum anteriorly.
- Each rib articulates posteriorly with two thoracic vertebrae by the costovertebral joint.
- Only the first rib articulates with the first thoracic vertebra.
- The first seven pairs of the ribs are attached directly to the sternum by costal cartilages and are called true ribs.
- The 8th, 9th, and 10th pairs indirectly articulate with the sternum and are called false ribs.
- The last two pairs of false ribs ( 11th and 12th ) are also known as floating ribs.
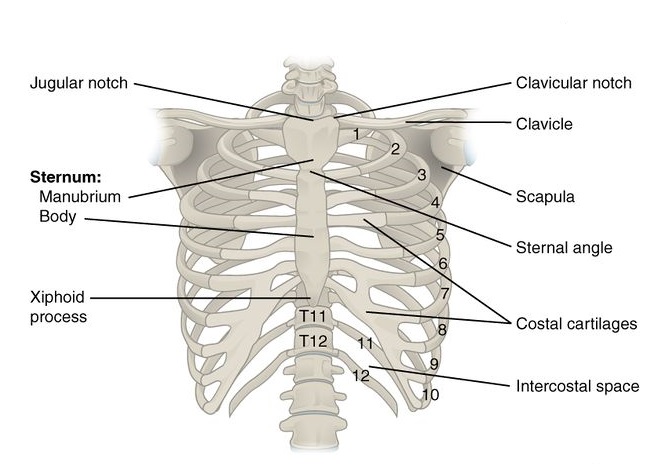
The Sternum
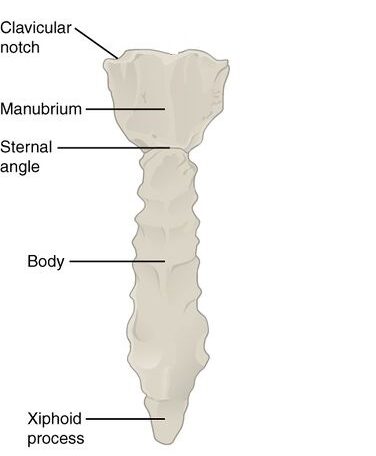
- The sternum is a T-shaped flat bone that is located centrally, in the anterior portion of the chest.
- The sternum has three segments:- manubrium, body and xiphoid process.
- The sternum connects the ribs via the costal cartilages forming the anterior rib cage.
There are a number of muscles related to ribs.
- intercostal muscles: situated in the intercostal spaces.
diaphragm: arises from the inner surfaces of the costal cartilages on the 6th rib
serratus anterior: originates from the 1st to 8th ribs
pectoralis major and minor muscles arise from superior anterior ribs
latissimus dorsi: originates from the 9th to 12th ribs
rectus abdominis: inserts at the 5th to 7th costal cartilages
Functions of the Ribs :-
They protect the organs within the thoracic cavity
They move superiorly, inferiorly, anteriorly and posteriorly to facilitate breathing (their flexibility in their movement increases/decreases the size of the thoracic cavity helping in the lungs in respiration.
Control of these movements is via the diaphragm, external intercostals, and the intercartilaginous portion of the internal intercostals.